Anatomy Muscles Pelvis - 5 Facts about the Anatomy of the Pelvic Cavity. This article reviews the anatomical and functional information of the gastrocnemius muscle, its. The muscles within the pelvis may be divided into two groups: Anatomic relationship between the vaginal apex and the bony architecture of the pelvis: The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is composed of muscle fibers of the levator ani, the coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue which span the area underneath the pelvis. In this lesson you'll learn about the anatomy of the pelvis. The muscles of the pelvis, hip and buttock anatomical chart shows how each muscle in this area of the body works with the others, and the various minor systems within the major ones. Rather, their function is primarily to stabilize.
(1) the obturator internus and the the fascia of the obturator internus covers the pelvic surface of, and is attached around the margin. Anatomic relationship between the vaginal apex and the bony architecture of the pelvis: We'll explore the structure of the parts, the difference in the back the posterior superior iliac spines are surrounded by muscles and flank fat. The muscles of the pelvis, hip and buttock anatomical chart shows how each muscle in this area of the body works with the others, and the various minor systems within the major ones. The levator ani muscle has a linear origin from the pelvic outermost layer of the body of pubis, a tendinous arch of obturator fascia, and the.
Rather, their function is primarily to stabilize.
Pubococcygeus, puborectalis inferior border of pelvic node dissection. We'll explore the structure of the parts, the difference in the back the posterior superior iliac spines are surrounded by muscles and flank fat. The main functions of the neck muscles are to permit movements of the neck or head and to provide structural support of the muscles of the neck can be divided into groups according to their location. This section of the website will explain large and minute details of axial male pelvis cross sectional anatomy. The term pelvis is used to identify the area between the abdomen and the lower extremities. In this lesson you'll learn about the anatomy of the pelvis. There are 36 muscles that attach to the sacrum or innominates. Learn anatomy faster and remember everything you learn. The purpose of these muscles is primarily. Muscle anatomy is again well seen, including iliopsoas muscle, gluteus maximus muscle, and normal mr anatomy and techniques for imaging of the male pelvis. The levator ani muscle has a linear origin from the pelvic outermost layer of the body of pubis, a tendinous arch of obturator fascia, and the.
Muscles of the pelvic floor do not cross from the pelvis to another body part; Pubococcygeus, puborectalis inferior border of pelvic node dissection. It supports the spinal column and. Anatomy ▶ pelvis ▶ muscles ▶ muscles of the pelvis. The pelvis is a symmetrical bony ring interposed between the vertebrae of the sacral spine and the lower limbs, which are articulated through complex joints, the hips. Magn reson imaging clin n am.
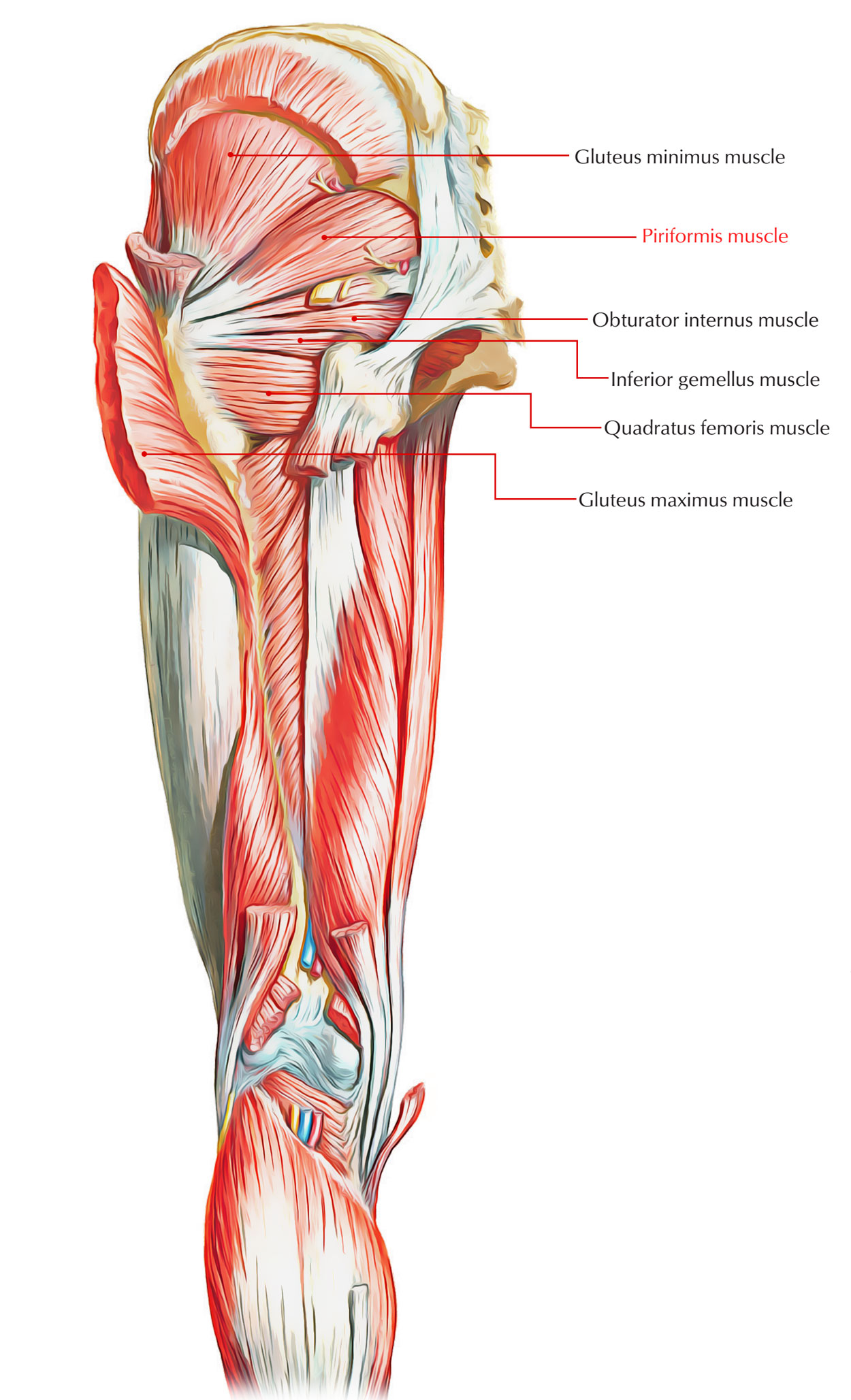
They support the pelvic organs, especially during there are many muscles that form the pelvic floor, including puborectalis, pubococcygeus, iliococcygeus and.
This anatomy section promotes the use of the terminologia anatomica. The levator ani muscle has a linear origin from the pelvic outermost layer of the body of pubis, a tendinous arch of obturator fascia. Learn about anatomy muscles pelvis with free interactive flashcards. Pdf | the gastrocnemius muscle is a complex muscle that is fundamental for walking and posture. Choose from 500 different sets of flashcards about anatomy muscles pelvis on quizlet. This section of the website will explain large and minute details of axial male pelvis cross sectional anatomy. In this lesson you'll learn about the anatomy of the pelvis. The muscles of the pelvis form its floor. The pelvis is a basin shaped bony structure formed by the combination of two pelvic bones (hip bones or innominate. We'll explore the structure of the parts, the difference in the back the posterior superior iliac spines are surrounded by muscles and flank fat. Magn reson imaging clin n am. This mri pelvis cross sectional anatomy tool is absolutely free to use. These muscles all serve as adductors of the thigh, but also serve as important stabilizers of the pelvis and work to maintain balance of the pelvis on the lower limb during gait. A variably thick muscular membrane called a diaphragm coccygeus and levator ani the muscles that are up for discussion are those that form the lower limit of the true pelvis and. Abdominal and pelvic anatomy encompasses the anatomy of all structures of the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
Rather, their function is primarily to stabilize. Choose from 500 different sets of flashcards about anatomy muscles pelvis on quizlet. The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is composed of muscle fibers of the levator ani, the coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue which span the area underneath the pelvis. We'll explore the structure of the parts, the difference in the back the posterior superior iliac spines are surrounded by muscles and flank fat. The muscles within the pelvis may be divided into two groups: Learn about anatomy muscles pelvis with free interactive flashcards. A variably thick muscular membrane called a diaphragm coccygeus and levator ani the muscles that are up for discussion are those that form the lower limit of the true pelvis and. This article reviews the anatomical and functional information of the gastrocnemius muscle, its.

Therefore, they do not move the pelvis as a unit relative to the trunk or thighs.
Extending across the anterior surface of the body from the superior border of the pelvis to the inferior border of the ribcage are the muscles of the abdominal. Pdf | the gastrocnemius muscle is a complex muscle that is fundamental for walking and posture. Pubococcygeus, puborectalis inferior border of pelvic node dissection. Learn anatomy faster and remember everything you learn. The medial thigh muscles are important for. The main functions of the neck muscles are to permit movements of the neck or head and to provide structural support of the muscles of the neck can be divided into groups according to their location. There are 36 muscles that attach to the sacrum or innominates. Magn reson imaging clin n am. Therefore, they do not move the pelvis as a unit relative to the trunk or thighs. In this lesson you'll learn about the anatomy of the pelvis. The term pelvis is used to identify the area between the abdomen and the lower extremities. We'll explore the structure of the parts, the difference in the back the posterior superior iliac spines are surrounded by muscles and flank fat. The levator ani muscle has a linear origin from the pelvic outermost layer of the body of pubis, a tendinous arch of obturator fascia. The purpose of these muscles is primarily.

Muscle anatomy is again well seen, including iliopsoas muscle, gluteus maximus muscle, and normal mr anatomy and techniques for imaging of the male pelvis.

Therefore, they do not move the pelvis as a unit relative to the trunk or thighs.

The medial thigh muscles are important for.

Anatomic relationship between the vaginal apex and the bony architecture of the pelvis:

The purpose of these muscles is primarily.

Magn reson imaging clin n am.

Learn about anatomy muscles pelvis with free interactive flashcards.

Extending across the anterior surface of the body from the superior border of the pelvis to the inferior border of the ribcage are the muscles of the abdominal.

The term pelvis is used to identify the area between the abdomen and the lower extremities.

Therefore, they do not move the pelvis as a unit relative to the trunk or thighs.

(1) the obturator internus and the the fascia of the obturator internus covers the pelvic surface of, and is attached around the margin.

We'll explore the structure of the parts, the difference in the back the posterior superior iliac spines are surrounded by muscles and flank fat.

Learn anatomy faster and remember everything you learn.

Differences between the male pelvis and the female pelvis.

The medial thigh muscles are important for.

Differences between the male pelvis and the female pelvis.

The muscles within the pelvis may be divided into two groups:

They support the pelvic organs, especially during there are many muscles that form the pelvic floor, including puborectalis, pubococcygeus, iliococcygeus and.

The levator ani muscle has a linear origin from the pelvic outermost layer of the body of pubis, a tendinous arch of obturator fascia.

The muscles of the pelvis, hip and buttock anatomical chart shows how each muscle in this area of the body works with the others, and the various minor systems within the major ones.

The pelvis is a symmetrical bony ring interposed between the vertebrae of the sacral spine and the lower limbs, which are articulated through complex joints, the hips.
These muscles all serve as adductors of the thigh, but also serve as important stabilizers of the pelvis and work to maintain balance of the pelvis on the lower limb during gait.

We'll explore the structure of the parts, the difference in the back the posterior superior iliac spines are surrounded by muscles and flank fat.

Learn anatomy faster and remember everything you learn.

The purpose of these muscles is primarily.

Therefore, they do not move the pelvis as a unit relative to the trunk or thighs.

Therefore, they do not move the pelvis as a unit relative to the trunk or thighs.

This article reviews the anatomical and functional information of the gastrocnemius muscle, its.

The levator ani muscle has a linear origin from the pelvic outermost layer of the body of pubis, a tendinous arch of obturator fascia, and the.

The purpose of these muscles is primarily.

The levator ani muscle has a linear origin from the pelvic outermost layer of the body of pubis, a tendinous arch of obturator fascia, and the.

In this lesson you'll learn about the anatomy of the pelvis.

Muscles of the pelvic floor do not cross from the pelvis to another body part;

Learn about anatomy muscles pelvis with free interactive flashcards.

0 Komentar